… provides a bootable pre-OS environment for testing BIOSes and in particular their initialization of Intel processors, hardware, and technologies. BITS can verify your BIOS against many Intel recommendations. In addition, BITS includes Intel’s official reference code as provided to BIOS, which you can use to override your BIOS’s hardware initialization with a known-good configuration, and then boot an OS.
http://biosbits.org/
Tag: intel
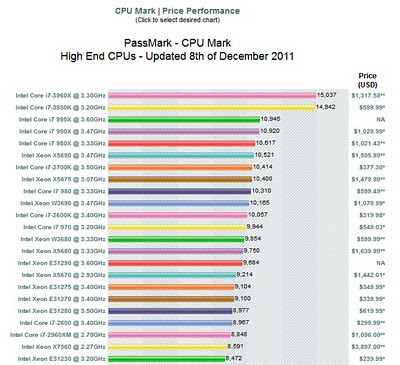
6 cores with Hyperthreading, up to 3.9 GHz burst mode, 15 MB Cache – this thing is awesome.
And the benchmark results to match:
results via this link
More specs at:
Intel� Core™ i7-3960X Processor Extreme Edition (15M Cache, 3.30 GHz)
AMD has released the first true 8 core processors. Current Intel i-series chips have up to 4 cores with Hyperthreading, which displays 8 cores to the OS. However, the new AMD architecture may ultimately provide some performance benefit in certain applications (such as rendering).
Initial benchmarks for the new ‘Bulldozer’ architecture show that they are roughly on-par with some of the midrange Intel offerings. However, the new processor architecture has the potential to offer significant gains as applications are optimized and as price points improve.
In Revit terms, more cores means faster rendering. In day to day computer terms, more cores means you can do more things faster.
In terms of technology and competition, I guess we can be glad that there are at least two big CPU manufacturers. If you want to read about their mutually assured destruction, check out this link.
More information about Bulldozer CPUs here:
Unlock Your Record Setting AMD FX Series Processor Today
and here
Bulldozer (microarchitecture) – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Found some very interesting information on Wikipedia about 32 bit and 64 bit processor architecture – check it out (italics by me):
AMD licensed its x86-64 design to Intel, where it is marketed under the name Intel 64 (formerly EM64T). AMD’s design replaced earlier attempts by Intel to design its own x86-64 extensions which had been referred to as IA-32e. As Intel licenses AMD the right to use the original x86 architecture (upon which AMD’s x86-64 is based), these rival companies now rely on each other for 64-bit processor development. This has led to a case of mutually assured destruction should either company refuse to renew the license. Should such a scenario take place, AMD would no longer be authorized to produce any x86 processors, and Intel would no longer be authorized to produce x86-64 processors, forcing it back to 32-bit x86 architecture. However, the agreement provides that if one party breaches the agreement it loses all rights to the other party’s technology while the other party receives perpetual rights to all licensed technology.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X86-64
If you want to read more about MAD, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mutually_assured_destruction